Buffered Definition Physics
PBS or phosphate-buffered saline is a buffer solution that is particularly valuable because it mimic the ion concentration osmolarity and pH of human body fluids. Definition of buffer Entry 2 of 4 1.
Unless soln is buffered.

Buffered definition physics. The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm of the molar hydrogen ion concentration. Noun 2 often attributive. Buffer solution or called buffer is one type of electrolyte solution that is very important in life.
Past simple and past participle of buffer 2. Have you ever imagined how the human body maintains its pH remained neutral because when the pH of human blood increases or decreases dramatically it will cause death. To provide protection against harm 3.
This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed.
Shocks of disappointment James Russell Lowell. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change.
In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions. Any of various devices or pieces of material for reducing shock or damage due to contact. May have served as a buffer against the.
Buffered Adjective Dissolved in a buffer solution. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.
A buffer is a chemical system designed to prevent dramatic alterations in fluid pH by binding up any changes in hydrogen ion concentrations due to excess acid or base production. You can explore more about buffer solutions here. Buffered Adjective Using a buffer.
One that protects by intercepting or moderating adverse pressures or influences. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer solutions are able to resist a significant change in pH when a limited concentration of acid or base is added to them.
In other words its isotonic to human solutions so its less likely to cause cell damage toxicity or unwanted precipitation in biological medical or biochemical research. Any substance or mixture of compounds that added to a solution is capable of neutralizing both acids and bases without appreciably changing the original acidity or alkalinity of the solution. A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer.
Buffer state a country separating two rival or hostile powers thought to prevent conflict between them Buffer zone a region separating two areas possibly to segregate or conjoin them Buffer navy a colloquial title Buffer an object that is used to polish and make shiny by rubbing. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH. Something that lessens or absorbs the shock of an impact.
Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. Also called buffer solution. A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution.
A solution containing such a substance. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
The most important characteristic of a buffer solution is its pH. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. A buffer may also be called a pH buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution.
Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change. A means or device used as a cushion against the shock of fluctuations in business or financial activity. Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa.
Buffer--a solution that resists pH change---Important for many reactions---eg enzymatic methods of analysis etc---ammonia is a base---so pH will increase as reaction proceeds. A sense of humor. Wiktionary 000 0 votes Rate this definition.
 What Is Data Buffer What Does Data Buffer Mean Data Buffer Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube
What Is Data Buffer What Does Data Buffer Mean Data Buffer Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube
 Salt Selection And Buffer Preparation Sigma Aldrich
Salt Selection And Buffer Preparation Sigma Aldrich
 How To Use A Guitar Buffer Pedal Effectrode
How To Use A Guitar Buffer Pedal Effectrode
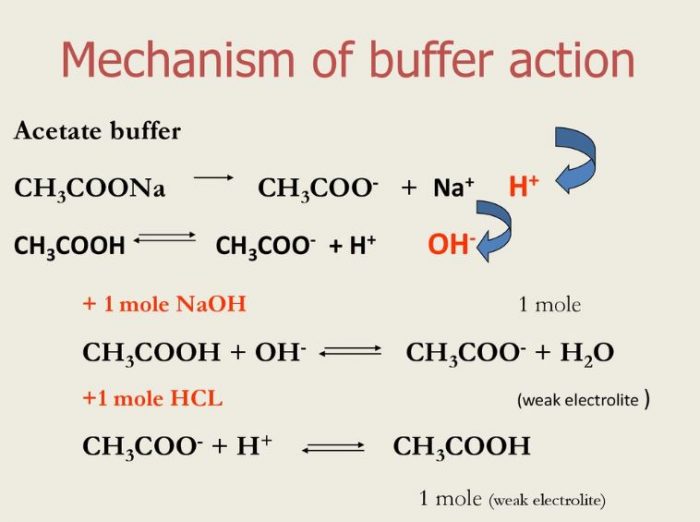 Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
 Climate Change Education Across The Curricula Across The Globelesson Plan Buffers Buffer Action And Ocean Acidification
Climate Change Education Across The Curricula Across The Globelesson Plan Buffers Buffer Action And Ocean Acidification
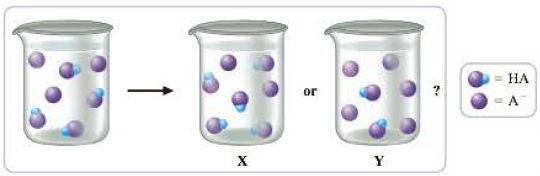 The Beaker On The Left Below Represents A Buffer Solution Of A Weak Acid Ha And Its Conjugate Base A Water Molecules And Spectator Ions Have Been Omitted For Clarity
The Beaker On The Left Below Represents A Buffer Solution Of A Weak Acid Ha And Its Conjugate Base A Water Molecules And Spectator Ions Have Been Omitted For Clarity
 Isocapnic Buffering Note Ve Pulmonary Ventilation Physiology Ventilation Lactation
Isocapnic Buffering Note Ve Pulmonary Ventilation Physiology Ventilation Lactation
 Chemistry Acids Bases Hydrolosis Of Salts And Buffers Flashcards Quizlet
Chemistry Acids Bases Hydrolosis Of Salts And Buffers Flashcards Quizlet
 Examples Of Buffer Solution In Everyday Life Their Applications And Uses
Examples Of Buffer Solution In Everyday Life Their Applications And Uses
 Lecture 22 The Digestive Tract Digestive System Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology
Lecture 22 The Digestive Tract Digestive System Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology
 10 6 Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
10 6 Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
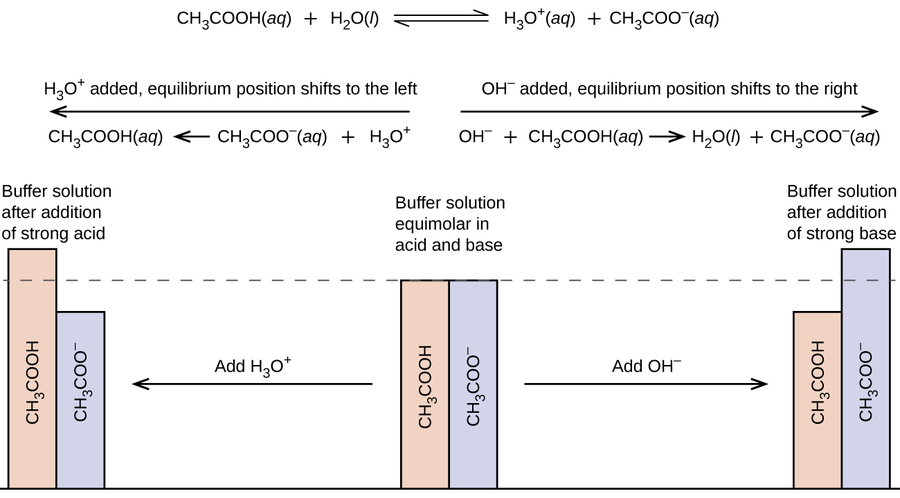 7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 What Is Buffering Computer Business Review
What Is Buffering Computer Business Review
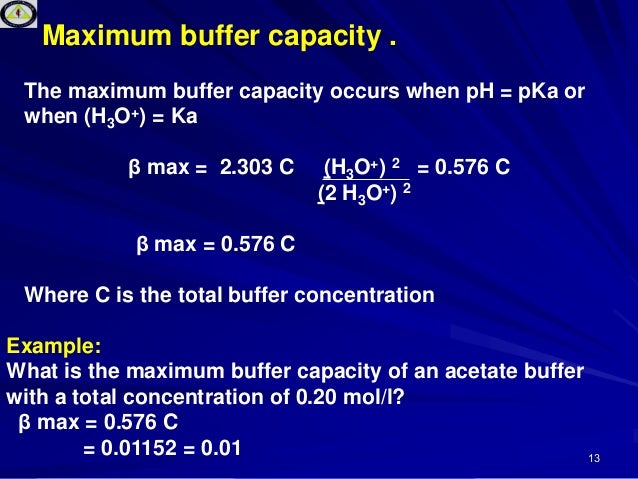
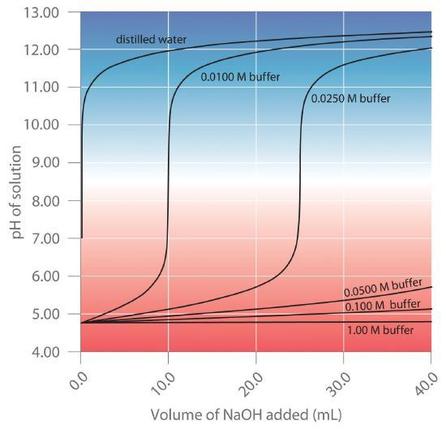 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts